What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is an evolving system that connects software, hardware, physical objects, and devices for communication, control, data collection, and exchange. It allows seamless interaction between humans and a variety of physical and virtual “things.” The term also refers to a vast network of “smart” objects. These objects are created by adding connectivity to traditional and non-traditional devices.
The Evolution and Importance of IoT
In recent years, IoT has become one of the most important technologies of the 21st century. It now encompasses billions of devices and internet-connected sensors. Examples include biometric medical devices, wearables, weather stations, city lighting systems, traffic lights, cameras, and sensors. Additionally, automation in industrial and agricultural production lines has expanded. According to IDC research, these devices are expected to exceed 55 billion by 2025. Furthermore, they will generate over half of the global data. This data, combined with increasing computing power, will fuel artificial intelligence systems. These systems will enhance coordination and foresight, ultimately improving daily life and boosting economic growth.
Modern IoT Applications
Modern IoT applications include smart cities, smart grid energy networks, smart homes, and smart healthcare, among others. As shown in Figure 1, these applications are shaping a new era of innovation.
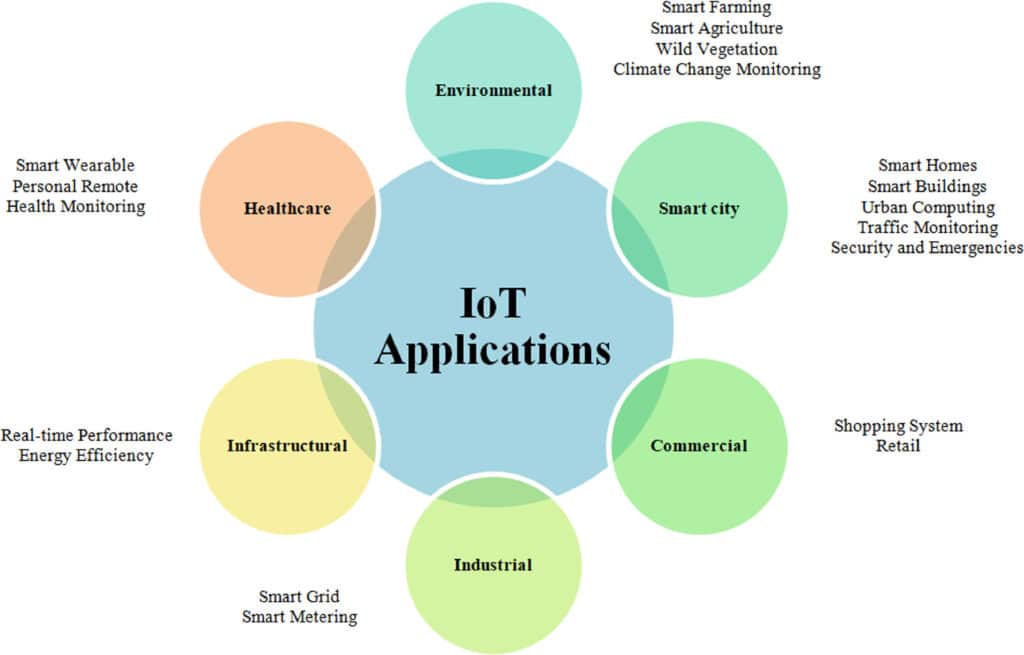
Advanced IoT Applications
Some IoT applications are abstract and describe a set of implementations that affect a unified space. However, these implementations do not necessarily interact with each other. A key example is the smart city. It includes smart networks, roads, lighting, public transportation, safety, environmental monitoring, smart parking, waste management, and more. Transforming a sector of human activity into a “smart” one is often an effective strategy for addressing issues, improving solutions, and fostering innovation.
The Future of IoT
An exciting new wave of IoT applications will emerge soon. These innovations will offer a more intuitive interface between humans and machines. Augmented reality (AR) applications, which have already started appearing, utilize 3D imagery, multi-channel sound, and touch. They will become our primary interface with the real world. The IoT will forever change how we interact with machines and each other. It will remove past barriers like time and distance. This will revolutionize various human activities, including housing, nutrition, health, industry, commerce, governance, and more.
[1] IDC Press release 27/06/2020 (Πρόσβαση 01/09/2021) – IoT Growth Demands Rethink of Long-Term Storage Strategies – https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prAP46737220
[2] Janani R.P., Renuka K., Aruna A., Lakshmi Narayanan K., 2021, IoT in Smart Cities: A Contemporary Survey, Global Transitions Proceedings, vol. 2, nr. 1, August 2021, KeAi,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gltp.2021.08.069

